
A new NCHS paper examines the implications of tacit engagement in humanitarian negotiations through the lens of two prevalent ethical challenges faced by humanitarian practitioners.

Join the annual Bergen Exchanges to explore how law serves as an instrument of change – and how it shapes and is shaped by power relations.

A new article for Global Governance: A Review of Multilateralism and International Organizations looks at the impact of multipolarity and the rise of regional and ad hoc coalitions on UN peacekeeping operations.

Edited by Cedric de Coning, Rui Saraiva and Ako Muto, this new book examines adaptive peacebuilding through case studies covering a range of conflicts across several continents.

The annual Arendalsuka is happening next week, where participants will discuss, debate and solve societal challenges, including humanitarian related challenges.

Interested in contributing to the next IHSA conference on “Humanitarianism in Changing Climates”? The call for papers is now open and will close on 15 September 2023.

In this latest episode of Talking Humanitarianism, humanitarian practitioner and researcher, Simon Robins, share his reflections on the operationalisation of justice within humanitarianism.
This NCHS paper explores the concept of humanitarian mediation, considering what it is in practice, how it differs from humanitarian negotiations and ethical implications.
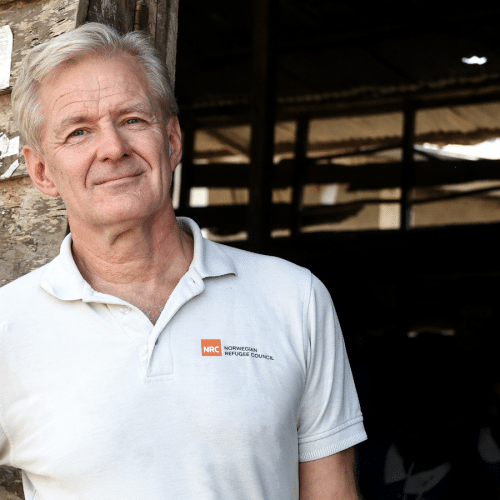

In this episode of Talking Humanitarianism, Jan Egeland, Secretary General of the Norwegian Refugee Council shares his experiences with humanitarian negotiations, particularly in Afghanistan and Syria.
In a new essay for Dædalus, Larissa Fast examines data sharing between humanitarians and donor governments in the context of humanitarian health delivery.
The fundamental dispute between Pakistan and Afghanistan is about their shared border, also known as the Durand Line, established by the British through the Durand Line agreement with Afghanistan in 1893. While Pakistan accepts it as an established international boundary, Afghanistan has yet to officially acknowledge it as such (noting Afghanistan has refrained from taking the matter to international platforms like the International Court of Justice). In Afghanistan, both Pashtun nationalists and groups identifying with political Islam, referred to as Islamists in this blog, refuse to officially recognise the border. Pakistan, however, actively supports Islamist groups to gain power in Afghanistan, while simultaneously opposing and undermining Pashtun nationalist political forces. This is a paradox that remains far from fully understood.
My latest research offers fresh insight into Pakistan’s preference for Afghan Islamists over Pashtun nationalists (Taj, 2022). The study shows there is a clash between the state identities of Pakistan and Afghanistan. Afghan Pashtun nationalists and Islamists approach this identity clash in different ways. Pakistan’s powerful military generals, who shape the country’s Afghan policy, favour the approach taken by the Afghan Islamists. This critical factor provides an important explanation for Pakistan’s unwavering support for Afghan Islamists, despite international pressure and the ensuing violent consequences within Pakistan.
For historical reasons, Pakistan’s core self-identity is Islamic, a stance that also serves pragmatic purposes. Being a multi-ethnic nation, the idea of Islam as state identity implies that Islam, as an overarching national identity, will overcome the prevailing ethnic differences in the society and result in a common Pakistani identity, which will curb the potential for secessionist tendencies on an ethnic basis. On the other hand, Afghanistan, also a multi-ethnic nation with an Islamic identity, centres its core self-identity around Pashtun ethnicity due to various historical reasons, despite the debates regarding its ethnic demographics (Shah, 2020).
The two states have different self-identities and they clash. Other Muslim countries have no problem with the Islamic identity of Pakistan but Afghanistan does. The reason is that a dominant section of Afghanistan’s own Pashtun population does not accept the Pashtun territory of Pakistan as part of Pakistan (Qassem and Durand, 2008). Since the era of Emir Dost Mohammad Khan (1826–39; 1843–63), a persistent Pashtun popular desire exists in Afghanistan that calls for reclaiming the ‘lost’ Pashtun territories. In Afghanistan, the popular Pashtun narratives about Pakistan are that Pakistan is an ‘unnatural state,’ a ‘British colonial project,’ and the ‘Punjab Regiment’ (of the British Indian army),’ which ‘uses’ Islam to ward off people’s attention from its ‘occupation’ of a part of the Pashtun land that belongs to Afghanistan.
Afghanistan finds it difficult to have its Pashtun self-identity continuously reaffirmed by its own dominant Pashtun public opinion, if it recognises the Pashtun areas in Pakistan, as an integral part of Pakistan. This predicament generates uncertainty within the Afghan state over its Pashtun identity, prompting it to challenge Pakistan’s Islamic identity and refuse the Durand Line as international border.
Afghanistan poses a challenge to the self-identity of Pakistan when Afghanistan asserts its self-proclaimed right to speak for the Pashtuns of Pakistan and refuses to recognise the border between the two countries. Pakistan has no problem with Afghanistan’s Pashtun identity, provided Afghanistan refrains from questioning Pakistan’s Islamic identity, which it does not. This is the clash of self-identities between the two countries that creates cognitive unease within both states. It quickly transforms into ontological insecurity — a fundamental uncertainty about self-identity.
When faced with anxiety over self-identity, states turn to self-identity-affirming routines, that seek to diminish doubts about self-identity (Chernobrov, 2016; Epstein, 2007). The routines help to bring a threatening environment under cognitive control. The routines may be peaceful or violent. Both Pakistan and Afghanistan have self-identity-affirming routines. Pakistan maintains relatively consistent routines, while some of Afghanistan’s routines fluctuate, depending on the incumbent power: nationalist or Islamist.
Initially, Pakistan adopted routinisation with Afghanistan through normal diplomatic relations and economic links. Yet, this approach proved ineffective due to Afghanistan’s refusal to acknowledge the border. Tensions often escalated, resulting in drastic incidents like diplomatic withdrawals, flag burnings, media campaigns, spy accusations, and sporadic border clashes. In response, Pakistan sought alternative avenues for routinisation of the relationship with Afghanistan.
One, Pakistan integrates Afghanistan into its animosity-driven relationship with India, viewing Afghanistan as a ‘brotherly Muslim’ state while labeling ‘Hindu’ India as an existential threat. Afghanistan’s stance on the Durand Line is thus seen by Pakistan as a part of Indian attempts to undermine Pakistan. Any Afghan attempts to voice concerns for Pakistani Pashtuns are swiftly rejected as ‘India-backed propaganda’. Thus publicly, Pakistan perceives Afghanistan not as a direct enemy, despite the latter’s stance on the Durand Line, but as a country where some elements aligned with India are hindering cordial relations between the states.
Two, Pakistan integrated Afghanistan into its relationship with the Western world, especially during the Cold War, leveraging Western concerns about the Soviet Union. Despite limited direct Soviet threats and no risk of domestic communism, Pakistan sought Western support for military aid, bolstering its stance against India and countering Afghanistan’s position on the Durand Line. This effort succeeded, gaining Cold War-era backing from the US and UK for Pakistan’s Durand Line stance.
Third, Pakistan established ties with Muslim countries to also reinforce its position on the Durand Line. Afghanistan’s efforts to rally Islamic support for its stance via collective Muslim platforms like the OIC (Organization of Islamic Cooperation) did not find backing from Muslim states (Ghaus, 1988).
Fourth, Pakistan has integrated a significant portion of its Pashtun population, especially in the settled districts (the area not adjacent to the Durand Line), a phenomenon known as ‘Pakistanisation.’ This term denotes the integration of Pashtuns into Pakistan’s state apparatus. Pashtuns constitute the second largest ethnic group in Pakistan’s armed forces and are also interwoven into the civil bureaucracy, prominent political parties, and in Karachi, the economic hub of Pakistan. They inhabit all corners of Pakistan. This ‘Pakistanisation’ consequently results in Pakistani Pashtuns giving little regard to Afghanistan’s self-declared assertions over Pakistani Pashtun territories.
One, Afghanistan uses the narratives of Pashtun nationalist intellectuals to bolster its self-identity. Since the 19th century, an abundance of Pashtun nationalist literature in Pashto language, encompassing poetry, prose, and music, has emerged, rejecting the Durand Line Agreement and aspiring for a Greater Afghanistan, encompassing Pakistani Pashtun areas. The Afghan state actively promotes these narratives in various public domains. Yet, rhetoric alone is not enough. Concrete actions are required for reaffirming self-identity, a challenge for Afghanistan due to its military weakness and economic dependence on Pakistan. This results in Afghanistan’s second routine: its ambiguous public stance towards Pakistani Pashtun areas.
The stance fluctuates between its three different positions depending upon the incumbent circumstances. Sometimes, it says, it wants Pashtunistan, or ‘full independence of the Pashtun area’. Sometimes, it says it wants ‘autonomous status of the area within the Pakistan federation’. Sometimes, it says ‘it is for the people [of the area] themselves to determine their future.’
Simultaneously, Afghanistan promptly complains about any violation of the Durand Line by Pakistan, although it also claims that it does not consider the Durand Line as an international border.
How do the approaches of Afghan Islamists and Pashtun nationalists differ in affirming the Afghan state’s self-identity? When Pashtun nationalists hold power, they publicly amplify the identity clash, engaging in diplomatic withdrawals, flag burnings, media campaigns, spy allegations, and occasional border skirmishes. Their narratives, steeped in Pashtun nationalist literature, idealise Greater Afghanistan based on the dismemberment of Pakistan, which is painted as the ‘evil other’, contrasting what Afghanistan stands for. In July 1949, the Afghan parliament, for the first of many times, officially repudiated the Durand Line and since then Afghan parliamentarians deliver fiery speeches against Pakistan. Afghan officials occasionally assert full territorial claims over Pakistan. All this creates cognitive anxiety for Pakistan, more precisely for Pakistan army generals, who control the country’s Afghan policy.
When Afghan Islamists hold power they avoid using public discourse and actions that accentuate identity clash with Pakistan. In other words, they remove the identity clash from the public view and restrict it to closed-door discussions with Pakistani authorities. This approach eases Pakistan’s, more precisely Pakistan army generals’, anxiety about their country’s self-identity and fosters smoother interactions between Pakistani generals and the Islamists in managing the contentious Pakistan-Afghanistan relationship.
The clash of identity viewpoint complements, not replaces, various other explanations about the two countries’ relations. The perspective explains why Islamists, such as the Taliban, despite being beholden to Pakistan for their power in Afghanistan, refuse to recognise the border between both countries. It also explains why Pakistan still supports the Taliban despite their non-recognition of the border.
Chernobrov, D. (2016). Ontological security and public (mis) recognition of international crises: Uncertainty, political imagining, and the self. Political psychology, 37(5), 581-596.
Epstein, N. (2007). Explaining the War on Terrorism from an Ontological-Security Perspective. MIT International Review, 1(1), 12-19.
Ghaus, A. S. (1988). The Fall of Afghanistan An Insider’s Account. PERGAMON-BRASSEY’S.
Qassem, A. S., & Durand, H. (2008). Pak-Afghan Relations: The Durand Line Issue. Policy Perspectives, 87-102.
Shah, I. A. (2020). Ethnic Make up in Afghanistan. Pashto, 49(659).
Taj, F. (2022). Clash of Identities: Ontological (In) Securities of Afghanistan and Pakistan, and the Repercussions. Policy Perspectives, 19(2), 1-20.