
In this article for Open Access Government, Antonio De Lauri (NCHS Director) discusses the purpose of humanitarian negotiations, diplomacy and the ethics of border control.

The 2022 edition of the WorldRiskReport includes contribution by NCHS associates, offering an overview of the digital risks in disaster situations.
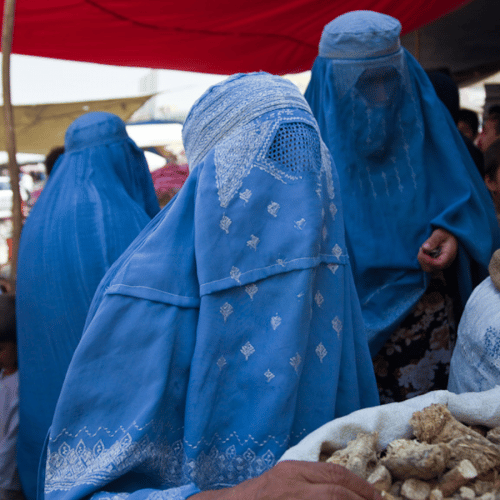

One year on from the Taliban taking control of Afghanistan and in the face of a growing humanitarian crisis, this PRIO blog discusses how Norway and the rest of the world should respond to the Taliban regime.

Report finds ‘Do no digital harm’ has emerged as an important humanitarian imperative, following contributions from PRIO project.

The war in Ukraine has significant consequences for food security in the Global South. This NUPI report examines how Norwegian aid partner countries’ food security is affected by the war.

NCHS associate, Ayşe Bala Akal, is set to present at an upcoming HHI webinar on security and risk analysis in humanitarian negotiations.

This seminar examines the impact of the EU’s external migration policies in Jordan, with a focus on competing priorities in education and employment.

You are invited to the launch of “Mediated Lives – Waiting and Hope Among Iraqi Refugees in Jordan” a book by Mirjam Twigt looking how ICTs play out in the everyday experiences of urban refugees.

You are invited to this breakfast seminar on 1 September discussing the impact of the EU’s external migration policies in Jordan. Held in-person in Bergen and online.

This paper examines Lebanon’s disaster response institutions and argues that the 2020 Beirut blast presents an opportunity to ‘build back better’ and overhaul contemporary institutional arrangements.
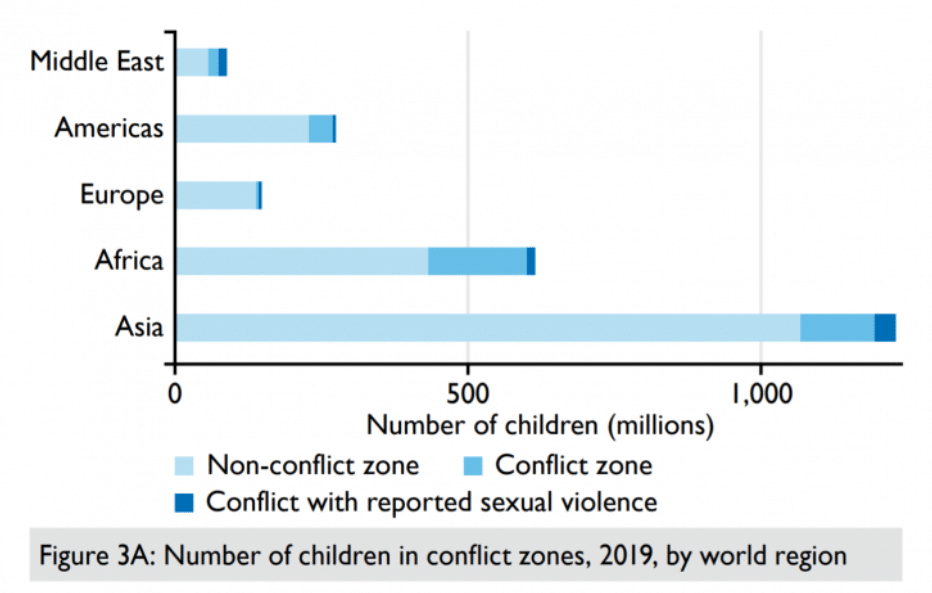
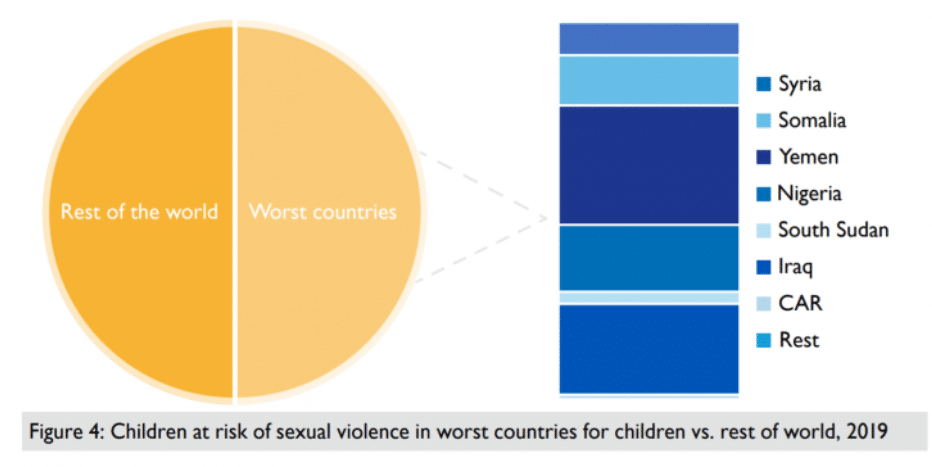
A staggering 72 million children—17% of the 426 million children living in conflict areas globally, or 1 in 6—are living near armed groups that have been reported to perpetrate sexual violence against children. That means 3% of all children in the world are living at risk for sexual violence in a conflict zone.
This is one of the figures of wartime risk reported in Save the Children’s 2021 report ‘Weapon of War: Sexual Violence Against Children in Conflict’. The figure is based on a new study conducted at the Peace Research Institute Oslo (PRIO).
concerning upward trend
This background study not only reveals an alarming reality, it identifies a concerning upward trend. This is a global problem that requires urgent attention. There are too few studies focusing on this problem or systematically documenting how children are victimized by sexual violence – directly or indirectly, how prevalent this is, and what the consequences are.
Globally, we estimate that in 2019 about 426 million children lived in a conflict zone, 50 kilometers or closer to violent conflict events. In some of these conflicts, the armed actors commit acts of sexual violence. A large majority of the conflicts with reports of sexual violence in recent years also have reports of children among the victims/survivors of sexual violence by armed actors.
The Sexual Violence in Armed Conflict (SVAC) dataset provides systematic data on the reported prevalence of sexual violence, and which conflict actors have been reported to commit sexual violence against children. The updated SVAC data covers all armed conflicts in the years 1989-2019.
Due to data limitations we do not know exactly how many children have been victimised of sexual violence, only where it has been reported and how pervasive the problem seems to be. Based on this, and using specific information on the location and timing of conflict events and population density we estimate how many children live in areas where conflict actors commit sexual violence against children.
The figure of 72 million children reflects the specific risk associated with sexual violence by actors directly involved in armed conflict, and does not account for risk of sexual violence committed by other types of perpetrators, such as sexual violence by criminal gangs, peacekeepers, law enforcement, or domestic sexual violence.
Sexual violence against children is a global problem that requires urgent attention. Policy makers, human rights defenders, and other actors need to devote more resources and dedicated attention to this vulnerable group of war victims to reduce the harm of war to children.
Specifically, we offer three recommendations:
As the child population at risk of wartime sexual violence seems to be increasing, the imperative to take action is more urgent than ever. As a member of the UN Security Council, and chairing the working group on Children in Armed Conflict, Norway now has a golden opportunity to contribute to this end. The Norwegian Minister of Foreign Affairs, Ine Eriksen Søreide, has promised to bring up the results from the report at the UN Security Council demanding that perpetrators of sexual violence in conflict be held accountable.